I am using Ubuntu 14.04. My internet connection is pretty slow (512 kbps). Sometimes I see that I have no software running which should download anything from the internet, but the system monitor still shows that some download is going on. So I think some hidden software are causing this. Is there a way I can monitor every software that is using internet?
-
@Braiam: That question is about monitoring *total* network data usage across system restarts. – David Foerster May 17 '17 at 13:21
-
@codeaviator: I think the answers on this question are better than on the one behind your link. We should either have the duplicate flag point the other way around or merge them altogether. I'm raising a flag for the latter. – David Foerster May 17 '17 at 13:22
-
@DavidFoerster Good point. I'm raising a moderator flag in favor of merging both questions. – codeaviator May 18 '17 at 04:49
-
1distro agnostic: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/368002/network-usage-top-htop-on-linux – Ciro Santilli OurBigBook.com Oct 29 '17 at 02:04
7 Answers
You can use nethogs  tool to monitor all your traffic on an interface.
tool to monitor all your traffic on an interface.
Install it using
sudo apt-get install nethogs
Now run it using
sudo nethogs <interface name>
For example
sudo nethogs wlan0
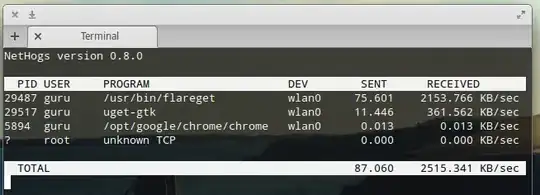
For more detail type man nethogs after installing.
-
-
No, this tool only monitors bandwidth. If you are looking for something similar to bandwidth shaping, you can refer [this](http://askubuntu.com/questions/20872/how-do-i-limit-internet-bandwidth) post. – g_p Jun 29 '15 at 18:16
-
3If you have 'creating socket failed while establishing local IP - are you root?' despite being root, then see the answer at http://askubuntu.com/a/729560/67747 – sage May 06 '16 at 16:36
-
-
1
I prefer sudo netstat -tunap
vinny@vinny-Bonobo-Extreme:~$ sudo netstat -tunap
[sudo] password for vinny:
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8200 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1160/minidlnad
tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 927/dnsmasq
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2543/cupsd
tcp 0 0 192.168.2.10:58491 198.252.206.149:443 ESTABLISHED 30401/firefox
tcp 0 0 192.168.2.10:39824 173.194.219.189:443 ESTABLISHED 30401/firefox
tcp 0 0 192.168.2.10:58569 198.252.206.149:443 ESTABLISHED 30401/firefox
tcp 0 0 192.168.2.10:59283 173.194.219.18:443 ESTABLISHED 30401/firefox
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 2543/cupsd
tcp6 1 0 ::1:60390 ::1:631 CLOSE_WAIT 863/cups-browsed
tcp6 1 0 ::1:34718 ::1:631 CLOSE_WAIT 1469/plasmashell
tcp6 1 0 ::1:60391 ::1:631 CLOSE_WAIT 863/cups-browsed
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1900 0.0.0.0:* 1160/minidlnad
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10097 0.0.0.0:* 26759/dhclient
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5353 0.0.0.0:* 759/avahi-daemon: r
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:39609 0.0.0.0:* 759/avahi-daemon: r
udp 0 0 192.168.2.10:57168 0.0.0.0:* 1160/minidlnad
udp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* 927/dnsmasq
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:* 26759/dhclient
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:631 0.0.0.0:* 863/cups-browsed
udp6 0 0 :::5353 :::* 759/avahi-daemon: r
udp6 0 0 :::13818 :::* 26759/dhclient
udp6 0 0 :::39404 :::* 759/avahi-daemon: r
shows even system proses that is using the network and the name of them.
but not really a monitor as you half to keep running it to see changing output.
- 18,154
- 6
- 56
- 69
- 252
- 2
- 5
-
-
As suggested below, [sudo watch -n1 netstat -tunap](https://askubuntu.com/questions/532424/how-to-monitor-bandwidth-usage-per-process) is a nice varation on this answer. – Josiah Yoder Feb 07 '22 at 13:10
-
Another [useful contribution](https://askubuntu.com/a/532431/226416): -n option is to show numerical address (ip) to which connection is established, -p is program which has established that connection, and -t lists all tcplimits to tcp connections. – Josiah Yoder Feb 07 '22 at 13:11
Just a bit more comfort with netstat sudo watch -n1 netstat -tunap
It will refresh the data each 1s
- 549
- 1
- 5
- 13
The iptraf utility is another way to monitor the traffic, provided by the iptraf  package.
package. sudo apt-get install iptraf installs it.
iptraf is available in Red Hat Linux also; run yum install iptraf as root to install it.
- 61
- 1
- 1
Terminal tool: netstat -tnp . -n option is to show numerical address (ip) to which connection is established, -p is program which has established that connection, and -t lists all tcplimits to tcp connections. Alternativelly, you could use netstat -a > networkscan.txt to output everything into a txt file
- 103,293
- 19
- 273
- 492
Socket Statistics, ss
ss is the modern alternative to netstat.
sudo apt install iproute2 # Install
Usage example:
watch -n1 sudo ss -ntp # Do not try to resolve service names. TCP. View processes
- 14,308
- 4
- 74
- 117
There is a more modern alternative to ss by now :)
- 1
-
2While this link may answer the question,it's better to include essential parts here. – Mar 16 '19 at 08:18